Posts tagged dna

Tag…You’re It!
Jan 19th
Classic genetics alone is unable to explain the diversity we see within a population of living things. This also cannot explain how identical twins with the same DNA sequences can have differences in their traits and development of disease. First introduced in 1939 by C.H. Waddington, epigenetics is now able to offer some explanation, as it studies the heritable changes in gene expression that are not due to any alteration in the DNA sequence.
This may help to answer many questions. How can we have so many different types of cells and they all carry the same genetic information? How is More >

Harnessing the power of bioinformatics in cancer research
Nov 22nd
One of the biggest challenges facing cancer researchers is that the disease varies so much from person to person. Even the same type of cancer – lung, brain, breast, colon, and so on – can be subtly different. This means that a therapy that works well in one patient may have no effect in another.
So researchers in the UK brought in the big guns – bioinformatics.
Cancer Research UK has set up seven British centers to start collecting 9,000 tumor samples from a wide range of cancer patients to create a DNA database. Researchers will extract DNA from these tumors and More >

One Size Does Not Fit All
Nov 11th
In 1994, there were more than 2.2 million serious medical cases, and over 100,000 deaths from negative reactions to prescribed drugs. (NCBI) These numbers have made adverse drug reactions one of the leading causes of hospitalization and deaths in the US. Currently, there is no easy way to determine how a patient is going to respond to a medication, so pharmaceutical companies are relying on a “one size fits all” policy. But as we can see with the amount of hospitalizations and deaths each year, there has to be a better way. One area that is shedding hope on this More >

The Medical Sleuth
Oct 31st
When we think of a detective the first thing that comes to mind is an investigator, either a member of a police agency or a private entity. However there are unique detectives within the multifaceted arena of medicine. All though we might already think of most doctors as detectives there are special doctors, units, working at the National Institute of Health’s (NIH) undiagnosed disease program. Doctors such as William A. Gahl at the NIH are disease detectives that try to elucidate the causes and genetic basis involved in the hundreds of unsolved and mysterious diseases that arise each year. Dr. Gahl More >

Autumn Leaves
Oct 28th
Autumn is my favorite season. I enjoy the cool weather, unpacking my sweaters from the attic and sleeping under my cozy comforter. But better than all of the above are the fantastic red, yellow and orange leaves that adorn the deciduous trees here in New York. Before I worked at the DNA Learning Center, this process was simply a beautiful rite of fall. Now, I see the whole process in a different light. It’s an elegant series of genetic steps that evolved millions of years ago, for a reason much bigger than beauty!
For most of the year, deciduous trees are More >

Model Organisms
Oct 12th
I asked a group of 5th graders the other day whether or not we can learn anything from studying other living things. For example, if we mutate or change the DNA of another organism, like fruit flies (D. melanogaster), can we learn anything about what can happen when human DNA changes? For this particular class, it seemed to be an absolutely absurd question. This could have been because the thought of fruit flies made them ill right before lunch, or they were unsure about how much we have in common with fruit flies.
So we got into a discussion about model More >

Can I Teach That?
Sep 21st
Recently I worked with a group of graduate students who volunteered to be science mentors for students in New York City. They were being trained in a small set of hands-on labs designed to introduce genetics in an engaging, informal environment. At some point during the training, we touched upon genetic mutations and variation. I mentioned that it was a perfect segway into discussion of natural selection and evolution. One participant raised her hand and asked, “Are we allowed to teach that?” My initial response was surprise. I said, “Of course!” It is unfortunate though, that as science educators we should even More >

Made to Order
Sep 12th
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) is a technique that allows scientists to screen embryos after fertilization through In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), to prevent the transmission of serious genetic diseases for couples who are at risk. It also can be used to screen the egg and sperm before fertilization occurs. Only unaffected embryos will be transferred to the uterus for implantation.
Image from Nature Reviews Genetics 3, 941-955 (December 2002)
While this technology offers the hope to increase the success of IVF, it does raise some concerns about choosing a child in order to meet the needs and desires of parents. While most cases seem to have More >
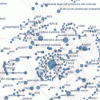
Cancer Genomics: so many mutations!
Feb 18th
The human genome is the complete collection of over three billion bases in each of our cells. Cancers accumulate multiple changes, or mutations, in their DNA that contribute to the disease by changing how cells behave. For instance, cancers need nutrients to grow. Very often, they get these nutrients by producing signals that encourage new blood vessel formation. Finding the mutations that lead to cancer is very difficult. For one thing, even for cancers that affect the same tissue and look similar, the mutations can be very different. Also, one of the hallmarks of cancer is an increased rate of More >

